Two of the most popular ways that the innovative and effective control of lights is achieved include photocells and motion sensors. Both have varying benefits depending on your needs. This article with contrast photocell and motion detectors focuses on their differences and similarities and the best uses for them.
Understanding Photocells

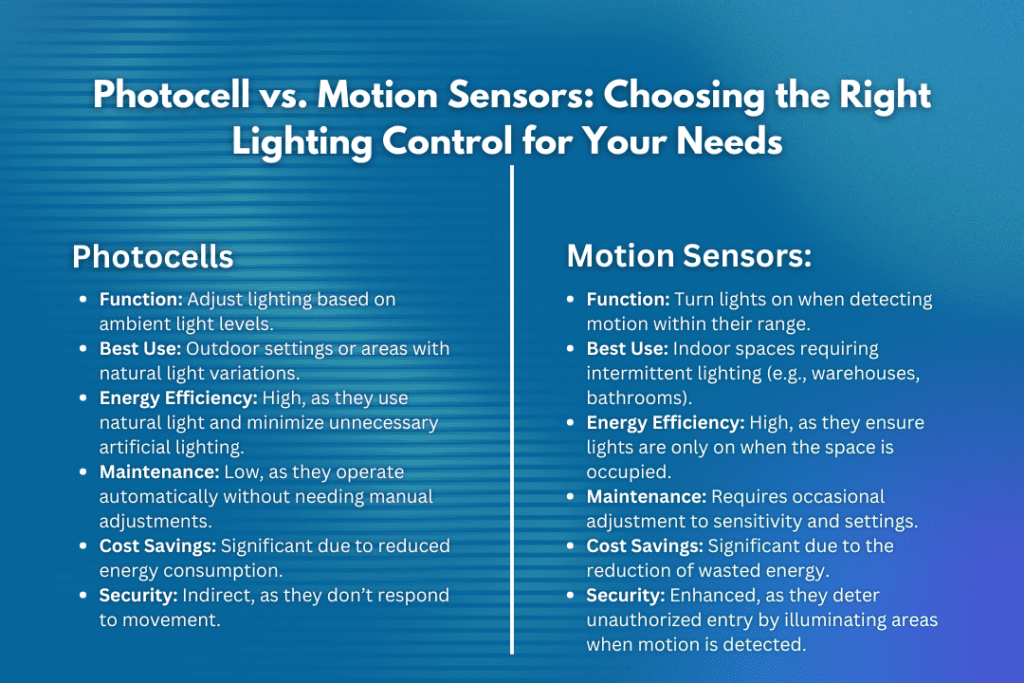
Photocells, also called light sensors or photoresistors, measure how much light is in the environment. The sensors respond by differences in the amount of natural light and thus drive the artificial lighting systems. It is simple: when the darkness falls outside, the lights turn themselves on, and when the sun threatens to appear again, the light turns itself off. This can also be referred to as a dusk-to-dawn feature. It saves energy because the light is only on when needed, and with a photocell, there is no need to depend on timers or people to turn the lights on and off.
Photocells, or light sensors and photoresistors, measure the prevailing light to adjust the contribution from artificial lighting. This process happens automatically so that lights switch on with dusk and off at dawn, therefore saving energy consumption without manual operation or timers.
Benefits of Photocells

Energy Efficiency:
Photocells prevent the wastage of energy by only turning on lights in case of inadequate light. This prevents the lights from turning on during the day or when natural light is adequate.

Low Maintenance:
Once set up, photocells only need a little maintenance because they recognize light intensity instead of motion.

Automation:
They can automatically control lights, which is good when it comes to outdoor lighting.

Cost Savings:
Since using less energy means paying less for utilities, photocells are an excellent choice in the long run.
Understanding Motion Sensors
Motion sensors, also called occupancy sensors, can tell when there is movement in their field of view. When these sensors sense motion, they turn on the lights. It makes them perfect for offices, hallways, warehouses, and any space that is only sometimes occupied. They make things easier and safer by ensuring lights only turn on when someone is in the area.
Benefits of Motion Sensors

Enhanced Security:
Motion sensors can deter break-ins by lighting up areas upon detecting motions. The sensors deter unauthorized entry by lighting up areas upon detecting motion.
Energy Savings:
The motion sensors turn off the lights whenever there is no movement for a certain duration. Turn off the lights in case of absence of activity automatically. This will prevent the waste of energy through unnecessary lighting.
Customization:
Many of the motion sensors are adjustable for sensitivity, time delay, and detecting range, thus providing more control over how the lights shall work. Allows for adjustable settings on sensitivity, delay, and detection range, thus allowing personalized control over lighting.
Indoor Applications:
Motion sensors do a great job in warehouses where there’s just no need to keep light everywhere at all times. If an area is unoccupied, the light can be dimmed to, say, 10% or turned fully off until the area is entered by someone. Other places where motion sensors succeed include bathrooms and meeting or storage areas. Excellently suited for controlled lighting in specific areas like warehouses, meeting rooms, and restrooms.
Choosing the Right Solution
The choice between photocells and motion sensors is determined by what purpose they are put to. Consider the following in making your choice:
Location:
Photocells work well when installed outdoors or in applications with large changes in natural light. Motion sensors lend themselves better to indoor applications where there is a need for lighting on an intermittent basis.
Energy Goals:
If saving energy is of paramount concern to you, then employ both means. Photocells maximize natural light, while motion monitors ensure that the lights do not stay on when they need not be.
Security Requirements:
Motion monitors add more security in that they light up places when there is any kind of movement detected. That, therefore, scares away would-be burglars.
Customization:
Most motion sensors can be adjusted for sensitivity and the time it takes to turn on after motion is detected, if you want more granular control over your light’s behavior.
Conclusion
Regarding controlling lights, photocells and motion sensors each have their strengths. Photocells work well outdoors and save energy, while motion sensors can make indoor lighting easier, safer, and more adjustable. Make the right choice by considering your needs and priorities, then pick the technology that best fits these. This will help you save on energy costs, be in a safer place at home, or improve the lights inside by using photocells and motion sensors.
Elevate Your Business with DVDLights
Partner with DVDLights to access premier solutions for commercial and horticultural lighting. Transform your industrial office with our advanced grow lights, designed to enhance plant growth and profitability. Contact us today to explore how our lighting solutions can revolutionize your business.
FAQs
Can photocells and motion sensors be used together?
Yes, combining both can provide comprehensive lighting control, maximizing energy savings and security.
How do photocells work in varying weather conditions?
Photocells are designed to adjust to changes in natural light, although extreme conditions (e.g., heavy fog) might affect performance temporarily.
Are motion sensors suitable for all types of indoor spaces?
While highly versatile, the effectiveness of motion sensors can depend on the space’s layout and occupancy patterns. Customization options can help optimize their use in diverse environments.
How do I decide between photocells and motion sensors for my project?
Consider the location, primary use case (e.g., security, energy efficiency), and whether the space is indoors or outdoors. Assessing these factors can help identify the most fitting technology.
Can these technologies contribute to LEED certification?
Yes, both photocells and motion sensors can play a significant role in achieving LEED certification by reducing energy consumption and enhancing building sustainability.





